NEXTFLEX® 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Kit 2.0
Fast and easy library prep protocol
Low input – Only 1 ng of input required
Multiplex up to 384 libraries
- Product description
- Kit Contents
- Citations
Ideal for Monitoring Populations of Microbial Communities
The NEXTFLEX® 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Library Prep Kit 2.0 is designed for the preparation of multiplexed amplicon libraries spanning the V4 hypervariable domain of microbial 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes. These libraries are compatible with paired-end sequencing on the Illumina® sequencing platforms.
Low Input Requirements for 16S rRNA Sequencing
As little as 1 ng of genomic DNA can be used to generate libraries using the NEXTflex 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Library Prep Kit 2.0.
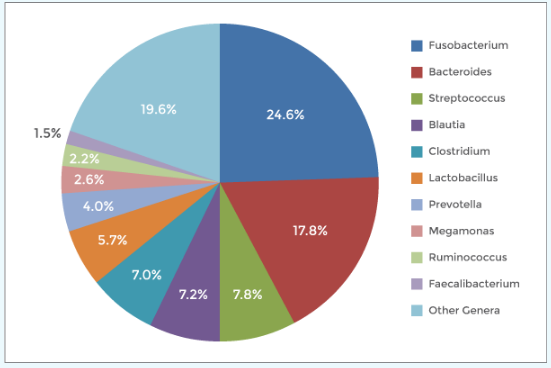
Optimized Protocol Offers Lower PCR Bias and Fewer Off-target Reads
The NEXTFLEX 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Kit 2.0 incorporates a second PCR step in the protocol for the addition of the sample-specific index which reduces off-target reads encountered during amplicon sequencing.
384 Barcodes Available for Cost-effective 16S V4 rRNA Sequencing
The NEXTFLEX 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Library Prep Kit 2.0 can be used for multiplexing up to 384 samples, to greatly reduce the cost of sequencing. The barcodes are offered in sets of 4, 12, 48 or 96 barcodes and supplied with 2 reactions worth of each barcode.
Features
Fast and easy library prep protocol
Low input – Only 1 ng of input required
Multiplex up to 384 libraries
Custom sequencing primers are not required
Automation protocols are now available for the Sciclone® NGS and NGSx Workstations to automate your 16S sequencing
Functionally validated with Illumina® sequencing platforms
Kit Specs
| Cat # | Name | Quantity |
| NOVA-4203-02 | NEXTflex™ 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Kit 2.0 (12 Barcodes) | 24 RXNS |
| NOVA-4203-03 | NEXTflex™ 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Kit 2.0 (48 Barcodes) | 96 RXNS |
| NOVA-4203-04 | NEXTflex™ 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Kit 2.0(Barcodes 1-96) | 192 RXNS |
| NOVA-4203-05 | NEXTflex™ 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Kit 2.0(Barcodes 97-192) | 192 RXNS |
| NOVA-4203-06 | NEXTflex™ 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Kit 2.0(Barcodes 193-288) | 192 RXNS |
| NOVA-4203-07 | NEXTflex™ 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Kit 2.0(Barcodes 289-384) | 192 RXNS |
KIT CONTENTS
NEXTFLEX® PCR Master Mix
NEXTFLEX® 16S V4 PCR I Primer Mix
NEXTFLEX® PCR II Barcoded Primer Mix
Resuspension Buffer
Nuclease-free Water
REQUIRED MATERIALS NOT PROVIDED
1 ng – 50 ng high-quality genomic DNA in up to 36 µL nuclease-free water for each library
96 well PCR Plate Non-skirted (Phenix Research, Cat # MPS-499) or similar
Adhesive PCR Plate Seal (Bio-Rad®, Cat # MSB1001)
Agencourt® AMPure® XP 5 mL (Beckman Coulter® Genomics, Cat # A63880)
Magnetic Stand – 96 (Thermo Fisher® Scientific, Cat # AM10027) or similar
Thermocycler
2, 10, 20, 200 and 1000 µL pipettes / multichannel pipettes
Nuclease-free barrier pipette tips
Vortex
80% Ethanol, freshly prepared (room temperature)
Selected Citations that Reference the Use of the NEXTFLEX 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq Kit 2.0
Bekker, V., Zwittink, R. D., Knetsch, C. W., Sanders, I. M., Berghuis, D., Heidt, P. J., . . . Kuijper, E. J. (2019). Dynamics of the Gut Microbiota in Children Receiving Selective or Total Gut Decontamination Treatment During Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.01.037.
Bruce-Keller, A. J., Fernandez-Kim, S., Townsend, R. L., Kruger, C., Carmouche, R., Newman, S., . . . Berthoud, H. (2017). Maternal obese-type gut microbiota differentially impact cognition, anxiety and compulsive behavior in male and female offspring in mice. Plos One, 12(4). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0175577.
Davey, M. P., Norman, L., Sterk, P., Huete-Ortega, M., Bunbury, F., Loh, B. K., . . . Smith, A. G. (2019). Snow algae communities in Antarctica – metabolic and taxonomic composition. New Phytologist. doi:10.1111/nph.15701.
Ford, S. L., Lohmann, P., Preidis, G. A., Gordon, P. S., Odonnell, A., Hagan, J., . . . Hair, A. B. (2019). Improved feeding tolerance and growth are linked to increased gut microbial community diversity in very-low-birth-weight infants fed mothers own milk compared with donor breast milk. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,109(4), 1088-1097. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqz006.
Luk, B., Veeraragavan, S., Engevik, M., Balderas, M., Major, A., Runge, J., . . . Versalovic, J. (2018). Postnatal colonization with human “infant-type” Bifidobacterium species alters behavior of adult gnotobiotic mice. Plos One, 13(5). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0196510.
Luna, R. A., Oezguen, N., Balderas, M., Venkatachalam, A., Runge, J. K., Versalovic, J., . . . Williams, K. C. (2017). Distinct Microbiome-Neuroimmune Signatures Correlate With Functional Abdominal Pain in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 3(2), 218-230. doi:10.1016/j.jcmgh.2016.11.008
Moon, C., Stupp, G. S., Su, A. I., & Wolan, D. W. (2017). Metaproteomics of colonic microbiota unveils discrete protein functions among colitic mice and control groups. doi:10.1101/219782.
Stalenhoef, J. E., et al. (2017) Fecal Microbiota Transfer for Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negatives: A Clinical Success Combined With Microbiological Failure. Open Forum Infectious Diseases, 4(2). doi:10.1093/ofid/ofx047.
Svensson, K., Paruch, L., Gaby, J. C., & Linjordet, R. (2018). Feeding frequency influences process performance and microbial community composition in anaerobic digesters treating steam exploded food waste. Bioresource Technology, 269, 276-284. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.096.
Sylvia, K. E., Deyoe, J. E., & Demas, G. E. (2018). Early-life sickness may predispose Siberian hamsters to behavioral changes following alterations of the gut microbiome in adulthood. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 73, 571-583. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2018.07.001.
Whon, T. W., Chung, W., Lim, M. Y., Song, E., Kim, P. S., Hyun, D., . . . Nam, Y. (2018). The effects of sequencing platforms on phylogenetic resolution in 16 S rRNA gene profiling of human feces. Scientific Data, 5, 180068. doi:10.1038/sdata.2018.68.
Wotzkas, S. Y., Kreuzer, M., Maier, L., Zuend, M., Schlumberger, M., Nguyen, B., . . . Misselwitz, B. (2018). Microbiota stability in healthy individuals after single-dose lactulose challenge – a randomized controlled study. doi:10.1101/424531.
Zhao, R., Yang, W., Pei, F., Zhao, L., & Hu, Q. (2018). In vitro fermentation of six kinds of edible mushrooms and its effects on fecal microbiota composition. Lwt, 96, 627-635. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2018.06.012.