riboPOOLs rRNA depletion for any species
rRNA depletion for any species
High complexity probes for efficient, reliable rRNA removal
Wide RNA-input range (10 ng – 3 µg)
riboPOOLs for highly degraded samples (FFPE)
- Product description
- Data
- Work flow
- Citations
riboPOOls' unique feature is their high complexity pooling approach based on our Pack Hunter design algorithm.
The high complexity of riboPOOLs ensures optimal and maximum rRNA coverage, allowing for efficient and cost-effective rRNA removal of any species or abundant RNA.
riboPOOLs are available for single species (e.g., Homo sapiens, Drosophila melanogaster, etc.) and multiple species.
Benefits of riboPOOLs
rRNA depletion for any species
Wide RNA-input range (10 ng – 3 µg)
High complexity probes for efficient, reliable rRNA removal
riboPOOLs for highly degraded samples (FFPE)
Cost-effective
special solution for ribosome profiling
Single-Species riboPOOLs
Single-species riboPOOLs are available for well-studied and lesser-known species (Escherichia coli, Arabidopsis thaliana or Schmidtea mediterranea and many more). Single-species riboPOOLs are specifically designed based on the species' rRNA to target both conserved and non-conserved regions.
Moreover, single species riboPOOLs are used on high quality to medium quality RNA and result in high rRNA depletion efficiency.
| Single Species riboPOOLs | |
Bacteria Escherichia coli Bacillus subtilis Caulobacter crescentus Clostridium perfringens Stenotrophomonas sp. Salmonella enterica Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Arthropoda Drosophila melanogaster Plautia stali Leptinotarsa decemlineata Ixodes scapular Aedes albopictus Apis mellifera Argiope bruennichi |
Archaea Haloferax volcanii | Cephalochordata Danio rerio |
Plants Oryza sativa Arabidopsis thaliana | Platyhelminthes Schmidtea mediterranea |
Vertebrata Mus musculus / R. norvegicus Homo sapiens sapiens Chinchilla lanigera Gallus gallus domesticus | Mollusca Crassostrea gigas Loripes orbiculatus and Lucinoma aequizonata (Clamps) |
Porifera Amphimedon queenslandica | Algea: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Cyanidioschyzon merolae Emiliania huxleyi |
| Fungi Saccharomyces cerevisiae Filamentous-Fungi Pichia pastoris Staphylococcus aureus Ustilago maydis Schizosaccharomyces pombe | Other: human Globin mRNA SARS-CoV-2 RNA |
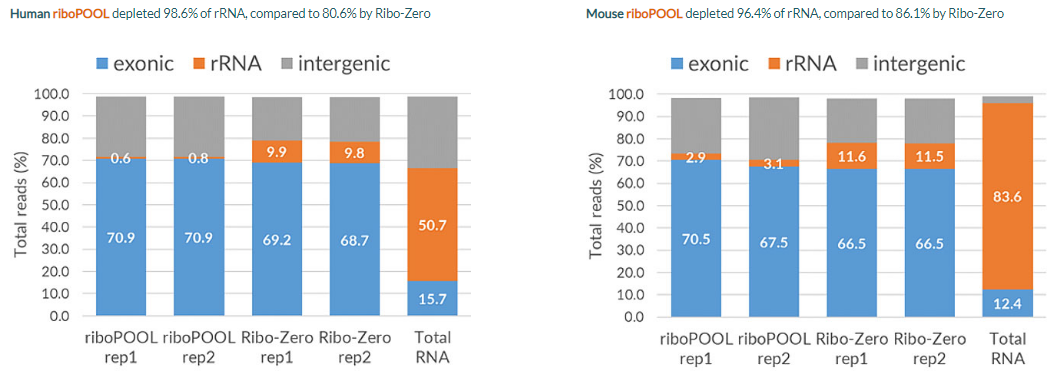
Specific, efficient rRNA depletion with riboPOOLs
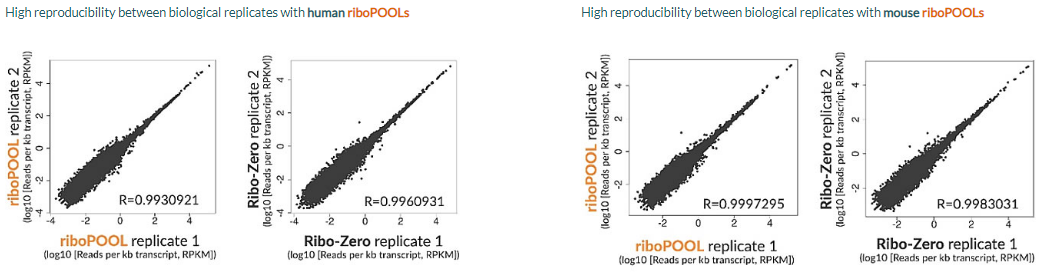
Reproducible results with riboPOOLs
riboPOOLs Special Applications
riboPOOLs can be customized to fit your RNA samples. We create riboPOOLs for any mixture of RNA (e.g., Seawater samples), strongly degraded RNA (i.e., FFPE samples), or ribosome profiling (Ribo-Seq) samples
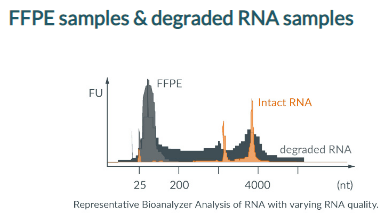
Total RNA extracted from FFPE tissue (Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues) are heavily degraded, with RIN values below 2.
Due to their strong fragmentation, ribosomal RNAs are difficult to remove before RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq).
With a gapless and tiled probe coverage of the entire rRNA sequence, siTOOLs Biotech developed an efficient rRNA depletion tool for FFPE and other strongly degraded RNA samples.
We currently have human, mouse/rat, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Drosophila melanogaster riboPOOLs for degraded RNA samples.
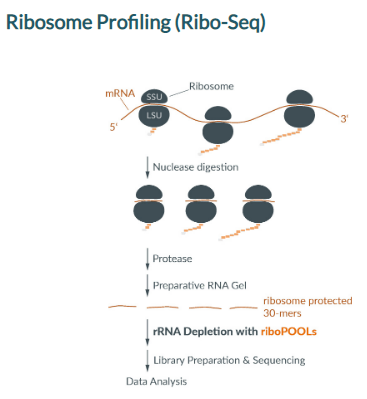
Ribosome Profiling (Ribo-Seq) identifies actively translated RNAs by sequencing only those 30-base mRNA fragments protected by ribosomes.
The nuclease digest, degrading unprotected mRNA outside of ribosomes, also generates highly abundant ribosomal RNA contaminations, making up many sequencing reads.
siTOOLs Biotech has generated an efficient Ribo-Seq riboPOOL targeting primarily those extremely abundant rRNA contaminants commonly found in Ribo-Seq samples.
The entire rRNA sequence is covered with capture probes to deplete any less abundant rRNA fragment.
Our Ribo-Seq riboPOOL portfolio includes rRNA removal solutions for human, mouse/rat, Drosophila melanogaster, and Caenorhabditis elegans Ribo-Seq samples.
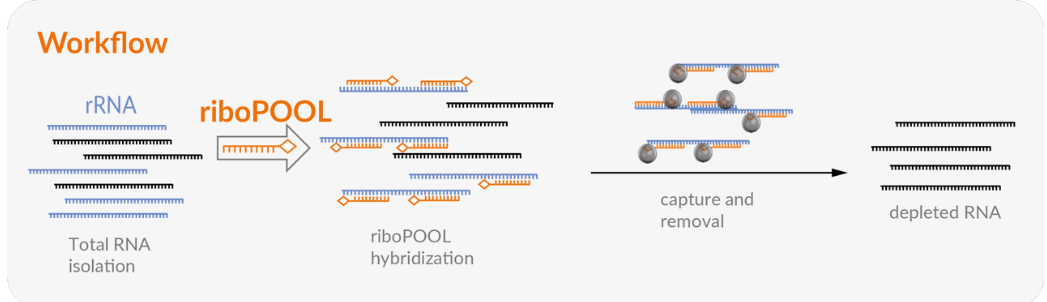
The riboPOOL workflow has four main steps:
1. Preparation of streptavidin-coated magnetic beads and riboPOOL
2. Hybridization of riboPOOL to target RNA
3. rRNA depletion
4. RNA Clean up.
All four steps can be completed within 70 minutes.
Achieve a fast and easy rRNA removal with riboPOOLs thanks to a hybridization-based workflow.
World Leading Scientist publish with riboPOOLs
scientific reports
Puiggené, Ò. et al. (2022) Extracellular degradation of a polyurethane oligomer involving outer membrane vesicles and further insights on the degradation of 2,4-diaminotoluene in Pseudomonas capeferrum TDA1
nature communications
M. A. Lawlo et al (2021) A transposon expression burst accompanies the activation of Y-chromosome fertility genes during Drosophila spermatogenesis
Genome Biology
Weipeng Mo et al. (2021) Landscape of transcription termination in Arabidopsis revealed by single-molecule nascent RNA sequencing
Dimitar Plamenov Petrov et al. (2021) Quantitative profiling and dynamics of mRNA modifications in Escherichia coli
Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry
Mio Takeuchi, Hideyoshi Yoshioka (2021) Acetate excretion by a methanotroph, Methylocaldum marinum S8, under aerobic conditions
Nature Protocols
Y. Long (2021) FLEP-seq: simultaneous detection of RNA polymerase II position, splicing status, polyadenylation site and poly(A) tail length at genome-wide scale by single-molecule nascent RNA sequencing
JBC
Neil Fleck & Christoph Grundner (2021) A Cas12a-based CRISPR interference system for multigene regulation in mycobacteria
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes
J. Andersen et al. (2021) Identification of small molecules that interfere with c-di-GMP signaling and induce dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms
Nature Communications
La Rosa et al. (2021) Compensatory evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa’s slow growth phenotype suggests mechanisms of adaptation in cystic fibrosis 12 3186
PLOS Genetics
Fuchs et al. (2021) Towards the characterization of the hidden world of small proteins in Staphylococcus aureus, a proteogenomics approach
BMC Genomics
Kim, I et al. (2019) Efficient depletion of ribosomal RNA for RNA sequencing in planarians 20, 909
RNA
Felix Grünberger et al. (2021) Nanopore sequencing of RNA and cDNA molecules in Escherichia coli
Microbiology Spectrum
Martin Gélinas et al. (2021) The de novo Purine Biosynthesis Pathway Is the Only Commonly Regulated Cellular Pathway during Biofilm Formation in TSBBased Medium in Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis
bioRxiv - preprint
Weihua Qin et. Al (2022) Probing protein ubiquitination in live cells
Ribosome profiling
Science
Bhat et al. (2021) Structural basis of ribosomal frameshifting during translation of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome
Nature Communications
Blaze et al. (2021) Neuronal Nsun2 deficiency produces tRNA epitranscriptomic alterations and proteomic shifts impacting synaptic signaling and behavior, 587, 14
Nat Protoc
Galmozzi, C. V. et al. (2019) Selective ribosome profiling to study interactions of translating ribosomes in yeast 14, 2279–2317
Nature Communications
Ryan. D et al. (2020) A high-resolution transcriptome map identifies small RNA regulation of metabolism in the gutmicrobe Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (20) 11